- Amen collagen capsules supplement offers 5 types of collagen (Type I, II, III, V, and X) all-in-one. Type 1 and 3 collagen may help support skin, hair and nails, Type 2 collagen may help support joints and cartilage, Type 5 and 10 may play a role to help support skin elasticity and firmness.*
- This collagen peptides supplement features premium sources of collagen, including grass-fed hydrolyzed bovine collagen peptides, organic chicken bone broth collagen, eggshell membrane collagen. This product doesn't contain shellfish.
- This collagen supplement also offers hyaluronic acid and vitamin C to help support skin, the immune system, and overall health.* Vitamin C can play an important role in collagen synthesis.*
- This multi collagen supplement is non-GMO, dairy, gluten, and soy-free. This collagen peptides supplement is also wheat-free, paleo and keto-friendly, making it suitable for various dietary restrictions.
- Manufactured in the USA with global ingredients in a cGMP-certified facility for quality and purity. Each bottle of Amen Collagen comes with 1 month of supply for daily use.
Amen Collagen.
- Amen collagen capsules supplement offers 5 types of collagen (Type I, II, III, V, and X) all-in-one. Type 1 and 3 collagen may help support skin, hair and nails, Type 2 collagen may help support joints and cartilage, Type 5 and 10 may play a role to help support skin elasticity and firmness.*
- This collagen peptides supplement features premium sources of collagen, including grass-fed hydrolyzed bovine collagen peptides, organic chicken bone broth collagen, eggshell membrane collagen. This product doesn't contain shellfish.
- This collagen supplement also offers hyaluronic acid and vitamin C to help support skin, the immune system, and overall health.* Vitamin C can play an important role in collagen synthesis.*
- This multi collagen supplement is non-GMO, dairy, gluten, and soy-free. This collagen peptides supplement is also wheat-free, paleo and keto-friendly, making it suitable for various dietary restrictions.
- Manufactured in the USA with global ingredients in a cGMP-certified facility for quality and purity. Each bottle of Amen Collagen comes with 1 month of supply for daily use.
Similar item to consider

Amen Leaky Gut+
$22.99Supplement Facts
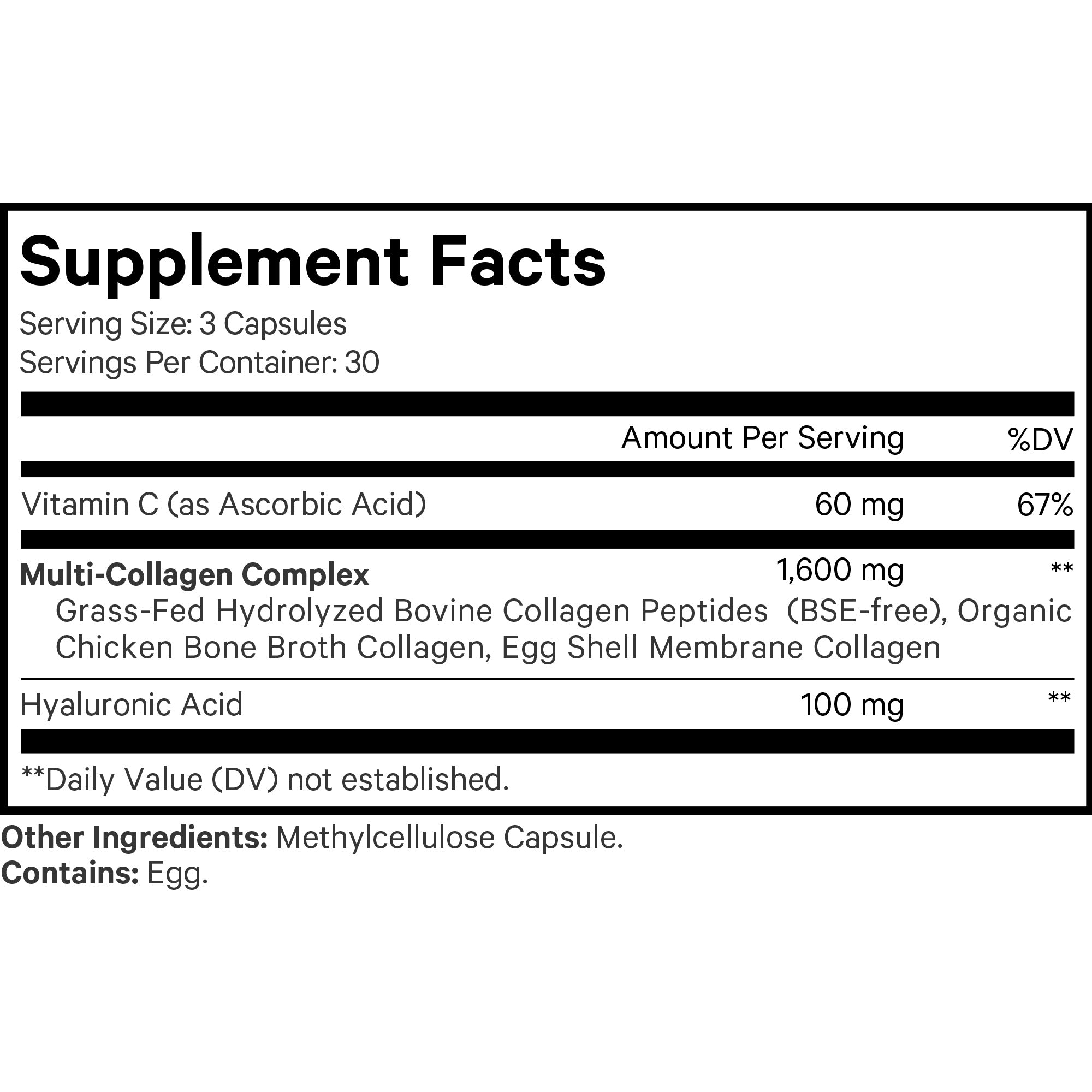
Ingredients
Multi-Collagen Complex: Grass-Fed Hydrolyzed Bovine Collagen Peptides, Organic Chicken Bone Broth Collagen, Egg Shell Membrane Collagen, Hyaluronic Acid. Other Ingredients: Methylcellulose Capsule.
Amino acid profile (average milligrams per serving): Alanine 139 mg, Arginine 118 mg, Aspartic Acid 89 mg, Glutamic Acid 157 mg, Glycine 374 mg, Histidine 12 mg, Hydroxylysine 14 mg, Hydroxyproline 182 mg, Isoleucine 24 mg, Leucine 46 mg, Lysine 57 mg, Methionine 14 mg, Phenylalanine 30 mg, Proline 217 mg, Serine 52 mg, Threonine 28 mg, Tyrosine 8 mg, Valine 35 mg. Contains eight of the nine essential amino acids. Doesn’t contain essential amino acid Tryptophan. Average milligrams per serving naturally occurring; absolute values may vary.
Contains: Egg.
Similar item to consider

Amen Leaky Gut+
$22.99EXPLORE MORE.
PRODUCT GALLERY.








Product Details
Supplement Facts

Ingredients
Multi-Collagen Complex: Grass-Fed Hydrolyzed Bovine Collagen Peptides, Organic Chicken Bone Broth Collagen, Egg Shell Membrane Collagen, Hyaluronic Acid. Other Ingredients: Methylcellulose Capsule.
Amino acid profile (average milligrams per serving): Alanine 139 mg, Arginine 118 mg, Aspartic Acid 89 mg, Glutamic Acid 157 mg, Glycine 374 mg, Histidine 12 mg, Hydroxylysine 14 mg, Hydroxyproline 182 mg, Isoleucine 24 mg, Leucine 46 mg, Lysine 57 mg, Methionine 14 mg, Phenylalanine 30 mg, Proline 217 mg, Serine 52 mg, Threonine 28 mg, Tyrosine 8 mg, Valine 35 mg. Contains eight of the nine essential amino acids. Doesn’t contain essential amino acid Tryptophan. Average milligrams per serving naturally occurring; absolute values may vary.
Contains: Egg.
Suggested Use
Take 3 capsules daily with 8 ounces of water or your favorite beverage. May be taken with or without food.
CAUTION: Do not exceed recommended dose. Please use caution if you have allergies or sensitivities to any of the listed ingredients. Pregnant or nursing mothers and individuals with a known medical condition should consult a physician before using this or any dietary supplement. Use only as directed. Some people might experience slight intolerance to marine or bovine product. If gastrointestinal discomfort (including bloating, cramps, diarrhea, or other digestive upset) or other sensitivity is experienced stop taking the product immediately. Some people are allergic to bovine (beef) or fish. If you are pregnant, nursing, or have a medical condition, please consult with your physician before use. If you have any questions about consuming this dietary supplement, consult with your health care professional before using. If you use prescription drugs or over-the-counter medications, are unaware of your current medical condition or have a pre-existing medical condition(s), consult with your health care professional before using. Discontinue use immediately if you experience any adverse symptoms or reactions while taking this product. Discontinue use 2 weeks prior to surgery. Do not use if your health status is unknown. Do not use if safety seal is damaged or missing. Keep out of reach of children and pets. Store in a cool, dry place, away from heat moisture. Use this product as a food supplement only. Do not use for weight reduction.
References
Grass-Fed Hydrolyzed Bovine Collagen Peptides
Vollmer DL, West VA, Lephart ED. Enhancing Skin Health: By Oral Administration of Natural Compounds and Minerals with Implications to the Dermal Microbiome. Int J Mol Sci. 2018;19(10):3059. Published 2018 Oct 7. doi: 10.3390/ijms19103059
Saha A, Alam MJ, Ashraf KU, Mannan A. Computational analysis of bovine alpha-1 collagen sequences. Bioinformation. 2013;9(1):42‐48. doi: 10.6026/97320630009042
León-López A, Morales-Peñaloza A, Martínez-Juárez VM, Vargas-Torres A, Zeugolis DI, Aguirre-Álvarez G. Hydrolyzed Collagen-Sources and Applications. Molecules. 2019;24(22):4031. Published 2019 Nov 7. doi: 10.3390/molecules24224031
K. Henriksen, M.A. Karsdal, in Biochemistry of Collagens, Laminins and Elastin, 2016
Albaugh VL, Mukherjee K, Barbul A. Proline Precursors and Collagen Synthesis: Biochemical Challenges of Nutrient Supplementation and Wound Healing. J Nutr. 2017;147(11):2011‐2017. doi:10.3945/jn.117.256404
Avila Rodríguez, MI, Rodríguez Barroso, LG, Sánchez, ML. Collagen: A review on its sources and potential cosmetic applications. J Cosmet. Dermatol. 2018; 17: 20– 26. DOI: 10.1111/jocd.12450
Paul C, Leser S, Oesser S. Significant Amounts of Functional Collagen Peptides Can Be Incorporated in the Diet While Maintaining Indispensable Amino Acid Balance. Nutrients. 2019;11(5):1079. Published 2019 May 15. doi: 10.3945/jn.117.256404
Proksch, E., Segger, D., Degwert, J., Schunck, M., Zague, V., & Oesser, S. (2014). Oral supplementation of specific collagen peptides has beneficial effects on human skin physiology: a double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Skin pharmacology and physiology, 27(1), 47–55. DOI: 10.1159/000351376
Zdzieblik D, Oesser S, Baumstark MW, Gollhofer A, König D. Collagen peptide supplementation in combination with resistance training improves body composition and increases muscle strength in elderly sarcopenic men: a randomised controlled trial. Br J Nutr. 2015;114(8):1237‐1245. doi: 10.1017/S0007114515002810
Daneault, A., Prawitt, J., Fabien Soulé, V., Coxam, V., & Wittrant, Y. (2017). Biological effect of hydrolyzed collagen on bone metabolism. Critical reviews in food science and nutrition, 57(9), 1922–1937. DOI: 10.1080/10408398.2015.1038377
Hexsel, Doris & Zague, Vivian & Schunck, Michael & Siega, Carolina & Camozzato, Fernanda & Oesser, Steffen. (2017). Oral supplementation with specific bioactive collagen peptides improves nail growth and reduces symptoms of brittle nails. Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology. DOI: 10.1111/jocd.12393
Yazaki M, Ito Y, Yamada M, et al. Oral Ingestion of Collagen Hydrolysate Leads to the Transportation of Highly Concentrated Gly-Pro-Hyp and Its Hydrolyzed Form of Pro-Hyp into the Bloodstream and Skin. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry. 2017 Mar;65(11):2315-2322. DOI: 10.1021/acs.jafc.6b05679
Organic Chicken Bone Broth
Crowley DC, Lau FC, Sharma P, et al. Safety and efficacy of undenatured type II collagen in the treatment of osteoarthritis of the knee: a clinical trial. Int J Med Sci. 2009;6(6):312‐321. Published 2009 Oct 9. doi: 10.7150/ijms.6.312
Bakilan F, Armagan O, Ozgen M, Tascioglu F, Bolluk O, Alatas O. Effects of Native Type II Collagen Treatment on Knee Osteoarthritis: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Eurasian J Med. 2016;48(2):95‐101. doi: 10.5152/eurasianjmed.2015.15030
Lugo, J.P., Saiyed, Z.M. & Lane, N.E. Efficacy and tolerability of an undenatured type II collagen supplement in modulating knee osteoarthritis symptoms: a multicenter randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Nutr J 15, 14 (2015). DOI: 10.1186/s12937-016-0130-8
Bagchi, D., Misner, B., Bagchi, M., Kothari, S. C., Downs, B. W., Fafard, R. D., & Preuss, H. G. (2002). Effects of orally administered undenatured type II collagen against arthritic inflammatory diseases: a mechanistic exploration. International journal of clinical pharmacology research, 22(3-4), 101–110.
Zhu, P., Li, X. Y., Wang, H. K., Jia, J. F., Zheng, Z. H., Ding, J., & Fan, C. M. (2007). Oral administration of type-II collagen peptide 250-270 suppresses specific cellular and humoral immune response in collagen-induced arthritis. Clinical immunology (Orlando, Fla.), 122(1), 75–84. DOI: 10.1016/j.clim.2006.08.004
Barnett, M. L., Kremer, J. M., St Clair, E. W., Clegg, D. O., Furst, D., Weisman, M., Fletcher, M. J., Chasan-Taber, S., Finger, E., Morales, A., Le, C. H., & Trentham, D. E. (1998). Treatment of rheumatoid arthritis with oral type II collagen. Results of a multicenter, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Arthritis and rheumatism, 41(2), 290–297. DOI: 10.1002/1529-0131(199802)41:2<290::AID-ART13>3.0.CO;2-R
Yoshinari, O., Moriyama, H., & Shiojima, Y. (2015). An overview of a novel, water-soluble undenatured type II collagen (NEXT-II). Journal of the American College of Nutrition, 34(3), 255–262. DOI: 10.1080/07315724.2014.919541
Paul, C., Leser, S., & Oesser, S. (2019). Significant Amounts of Functional Collagen Peptides Can Be Incorporated in the Diet While Maintaining Indispensable Amino Acid Balance. Nutrients, 11(5), 1079. DOI: 10.3390/nu11051079
Darling, A. L., Manders, R., Sahni, S., Zhu, K., Hewitt, C. E., Prince, R. L., Millward, D. J., & Lanham-New, S. A. (2019). Dietary protein and bone health across the life-course: an updated systematic review and meta-analysis over 40 years. Osteoporosis international : a journal established as result of cooperation between the European Foundation for Osteoporosis and the National Osteoporosis Foundation of the USA, 30(4), 741–761. DOI: 10.1007/s00198-019-04933-8
Lerman, R. H., Chang, J. L., Konda, V., Desai, A., & Montalto, M. B. (2015). Nutritional Approach for Relief of Joint Discomfort: A 12-week, Open-case Series and Illustrative Case Report. Integrative medicine (Encinitas, Calif.), 14(5), 52–61. PMCID: PMC4712866
Egg Shell Membrane Collagen
Ruff KJ, Morrison D, Duncan SA, Back M, Aydogan C, Theodosakis J. Beneficial effects of natural eggshell membrane versus placebo in exercise-induced joint pain, stiffness, and cartilage turnover in healthy, postmenopausal women. Clin Interv Aging. 2018;13:285‐295. Published 2018 Feb 19. doi: 10.2147/CIA.S153782
Ruff KJ, Winkler A, Jackson RW, DeVore DP, Ritz BW. Eggshell membrane in the treatment of pain and stiffness from osteoarthritis of the knee: a randomized, multicenter, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical study. Clin Rheumatol. 2009;28(8):907‐914. doi: 10.1007/s10067-009-1173-4
Hewlings, S., Kalman, D., & Schneider, L. V. (2019). A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled, Prospective Clinical Trial Evaluating Water-Soluble Chicken Eggshell Membrane for Improvement in Joint Health in Adults with Knee Osteoarthritis. Journal of medicinal food, 22(9), 875–884. DOI: 10.1089/jmf.2019.0068
Ruff, K. J., DeVore, D. P., Leu, M. D., & Robinson, M. A. (2009). Eggshell membrane: a possible new natural therapeutic for joint and connective tissue disorders. Results from two open-label human clinical studies. Clinical interventions in aging, 4, 235–240. DOI: 10.2147/cia.s5797
Hyaluronic Acid
Papakonstantinou E, Roth M, Karakiulakis G. Hyaluronic acid: A key molecule in skin aging. Dermatoendocrinol. 2012;4(3):253‐258. doi: 10.4161/derm.21923
Oe M, Sakai S, Yoshida H, et al. Oral hyaluronan relieves wrinkles: a double-blinded, placebo-controlled study over a 12-week period. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2017;10:267‐273. Published 2017 Jul 18. doi: 10.2147/CCID.S141845
Jegasothy SM, Zabolotniaia V, Bielfeldt S. Efficacy of a New Topical Nano-hyaluronic Acid in Humans. J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2014;7(3):27‐29. PMID: 24688623
Gupta RC, Lall R, Srivastava A, Sinha A. Hyaluronic Acid: Molecular Mechanisms and Therapeutic Trajectory. Front Vet Sci. 2019;6:192. Published 2019 Jun 25. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2019.00192
Kawada C, Yoshida T, Yoshida H, et al. Ingested hyaluronan moisturizes dry skin. Nutr J. 2014;13:70. Published 2014 Jul 11. doi: 10.1186/1475-2891-13-70
Bowman S, Awad ME, Hamrick MW, Hunter M, Fulzele S. Recent advances in hyaluronic acid based therapy for osteoarthritis. Clin Transl Med. 2018;7(1):6. Published 2018 Feb 16. doi: 10.1186/s40169-017-0180-3
Tashiro T, Seino S, Sato T, Matsuoka R, Masuda Y, Fukui N. Oral administration of polymer hyaluronic acid alleviates symptoms of knee osteoarthritis: a double-blind, placebo-controlled study over a 12-month period. ScientificWorldJournal. 2012;2012:167928. doi: 10.1100/2012/167928
Altman, R., Hackel, J., Niazi, F., Shaw, P., & Nicholls, M. (2018). Efficacy and safety of repeated courses of hyaluronic acid injections for knee osteoarthritis: A systematic review. Seminars in arthritis and rheumatism, 48(2), 168–175. DOI: 10.1016/j.semarthrit.2018.01.009
Concoff, A., Sancheti, P., Niazi, F., Shaw, P., & Rosen, J. (2017). The efficacy of multiple versus single hyaluronic acid injections: a systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC musculoskeletal disorders, 18(1), 542. DOI: 10.1186/s12891-017-1897-2
Altman, R. D., Bedi, A., Karlsson, J., Sancheti, P., & Schemitsch, E. (2016). Product Differences in Intra-articular Hyaluronic Acids for Osteoarthritis of the Knee. The American journal of sports medicine, 44(8), 2158–2165. DOI: 10.1177/0363546515609599
Witteveen, A. G., Hofstad, C. J., & Kerkhoffs, G. M. (2015). Hyaluronic acid and other conservative treatment options for osteoarthritis of the ankle. The Cochrane database of systematic reviews, (10), CD010643. DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD010643.pub2
Maheu, E., Rannou, F., & Reginster, J. Y. (2016). Efficacy and safety of hyaluronic acid in the management of osteoarthritis: Evidence from real-life setting trials and surveys. Seminars in arthritis and rheumatism, 45(4 Suppl), S28–S33. DOI: 10.1016/j.semarthrit.2015.11.008
Vitamin C
Wu M, Cronin K, Crane JS. Biochemistry, Collagen Synthesis. [Updated 2020 Apr 6]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2020 Jan-.
Boyera, N., Galey, I., & Bernard, B. A. (1998). Effect of vitamin C and its derivatives on collagen synthesis and cross-linking by normal human fibroblasts. International journal of cosmetic science, 20(3), 151–158. DOI: 10.1046/j.1467-2494.1998.171747.x
Lis, D. M., & Baar, K. (2019). Effects of Different Vitamin C-Enriched Collagen Derivatives on Collagen Synthesis. International journal of sport nutrition and exercise metabolism, 29(5), 526–531. DOI: 10.1123/ijsnem.2018-0385
Kleszczewska E. (2007). Biologiczne znaczenie witaminy C ze szczególnym z uwzglednieniem jej znaczenia w metabolizmie skóry [Biological role and importance in the skin metabolism of vitamin C]. Polski merkuriusz lekarski : organ Polskiego Towarzystwa Lekarskiego, 23(138), 462–465. PMID: 18432133
DePhillipo NN, Aman ZS, Kennedy MI, Begley JP, Moatshe G, LaPrade RF. Efficacy of Vitamin C Supplementation on Collagen Synthesis and Oxidative Stress After Musculoskeletal Injuries: A Systematic Review. Orthop J Sports Med. 2018;6(10):2325967118804544. Published 2018 Oct 25. doi: 10.1177/2325967118804544
Moores J. (2013). Vitamin C: a wound healing perspective. British journal of community nursing, Suppl, S6–S11. DOI: 10.12968/bjcn.2013.18.sup12.s6
Collins N. (2004). Adding vitamin C to the wound management mix. Advances in skin & wound care, 17(3), 109–112. DOI: 10.1097/00129334-200404000-00010
Ronchetti, I. P., Quaglino, D., Jr, & Bergamini, G. (1996). Ascorbic acid and connective tissue. Sub-cellular biochemistry, 25, 249–264. DOI: 10.1007/978-1-4613-0325-1_13
Vaxman, F., Olender, S., Lambert, A., Nisand, G., & Grenier, J. F. (1996). Can the wound healing process be improved by vitamin supplementation? Experimental study on humans. European surgical research. Europaische chirurgische Forschung. Recherches chirurgicales europeennes, 28(4), 306–314. DOI: 10.1159/000129471
Hallberg, L., Brune, M., & Rossander, L. (1989). The role of vitamin C in iron absorption. International journal for vitamin and nutrition research. Supplement = Internationale Zeitschrift fur Vitamin- und Ernahrungsforschung. Supplement, 30, 103–108. PMID: 2507689
Lynch, S. R., & Cook, J. D. (1980). Interaction of vitamin C and iron. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences, 355, 32–44. DOI: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1980.tb21325.x
Teucher, B., Olivares, M., & Cori, H. (2004). Enhancers of iron absorption: ascorbic acid and other organic acids. International journal for vitamin and nutrition research. Internationale Zeitschrift fur Vitamin- und Ernahrungsforschung. Journal international de vitaminologie et de nutrition, 74(6), 403–419. DOI: 10.1024/0300-9831.74.6.403
Carr, A. C., & Maggini, S. (2017). Vitamin C and Immune Function. Nutrients, 9(11), 1211. DOI: 10.3390/nu9111211
Ströhle, A., & Hahn, A. (2009). Vitamin C und Immunfunktion [Vitamin C and immune function]. Medizinische Monatsschrift fur Pharmazeuten, 32(2), 49–56. PMID: 19263912
EXPLORE MORE.

Multi collagen
capsules.
SUGGESTED USE.
Take 3 capsules daily with 8 ounces of water or your favorite beverage. May be taken with or without food.
CAUTION: Do not exceed recommended dose. Please use caution if you have allergies or sensitivities to any of the listed ingredients. Pregnant or nursing mothers and individuals with a known medical condition should consult a physician before using this or any dietary supplement. Use only as directed. Some people might experience slight intolerance to marine or bovine product. If gastrointestinal discomfort (including bloating, cramps, diarrhea, or other digestive upset) or other sensitivity is experienced stop taking the product immediately. Some people are allergic to bovine (beef) or fish. If you are pregnant, nursing, or have a medical condition, please consult with your physician before use. If you have any questions about consuming this dietary supplement, consult with your health care professional before using. If you use prescription drugs or over-the-counter medications, are unaware of your current medical condition or have a pre-existing medical condition(s), consult with your health care professional before using. Discontinue use immediately if you experience any adverse symptoms or reactions while taking this product. Discontinue use 2 weeks prior to surgery. Do not use if your health status is unknown. Do not use if safety seal is damaged or missing. Keep out of reach of children and pets. Store in a cool, dry place, away from heat moisture. Use this product as a food supplement only. Do not use for weight reduction.






































 Start a live chat
Start a live chat
 1-856-CODEAGE
1-856-CODEAGE























